vsomeip的event分析
整体框架
各模块之间的关系
classDiagram
class routing_host {
<<Abstract>>
}
class routing_manager {
<<Abstract>>
}
class routing_manager_base {
<<Abstract>>
-routing_manager_host *host_
}
routing_manager_base --> routing_manager_host : Association
routing_manager <|-- routing_manager_base : Inheritance
routing_host <|-- routing_manager_base : Inheritance
class routing_manager_client {
}
routing_manager_base <|-- routing_manager_client : Inheritance
class routing_manager_impl {
-std::shared_ptr~routing_manager_stub~ stub_
-std::shared_ptr~sd::service_discovery~ discovery_
-std::shared_ptr~endpoint_manager_impl~ ep_mgr_impl_
}
routing_manager_base <|-- routing_manager_impl : Inheritance
service_discovery_host <|-- routing_manager_impl : Inheritance
routing_manager_stub_host <|-- routing_manager_impl : Inheritance
routing_manager_impl o-- service_discovery : Aggregation
routing_manager_impl o-- routing_manager_stub : Aggregation
routing_manager_impl o-- endpoint_manager_impl : Aggregation
class application {
<<Abstract>>
}
class application_impl {
-std::shared_ptr~routing_manager~ routing_
}
application <|-- application_impl : Inheritance
routing_manager_host <|-- application_impl : Inheritance
application_impl o-- routing_manager : Aggregation
class endpoint_host {
<<Abstract>>
}
class endpoint_manager_base {
-routing_manager_base* const rm_
-std::map~client_t, std::shared_ptr~endpoint~~ local_endpoints_
}
endpoint_host <|-- endpoint_manager_base : Inheritance
endpoint_manager_base --> routing_manager_base : Association
endpoint_manager_base o-- endpoint : Aggregation
class endpoint_manager_impl {
-client_endpoints_by_ip_t client_endpoints_by_ip_
-erver_endpoints_t server_endpoints_
}
endpoint_manager_base <|-- endpoint_manager_impl : Inheritance
endpoint_manager_impl o-- endpoint : Aggregation
namespace sd {
class service_discovery_host
class service_discovery
class service_discovery_impl
}
class service_discovery_host {
<<Abstract>>
}
class service_discovery {
<<Abstract>>
}
class service_discovery_impl {
service_discovery_host *host_
}
service_discovery <|-- service_discovery_impl : Inheritance
service_discovery_impl --> service_discovery_host : Association
class routing_manager_stub_host {
}
class routing_manager_stub {
-routing_manager_stub_host *host_
}
routing_host <|-- routing_manager_stub : Inheritance
routing_manager_stub --> routing_manager_stub_host : Association
class endpoint {
<<Abstract>>
}
class endpoint_impl {
<<Abstract>>
-std::weak_ptr~endpoint_host~ endpoint_host_
-std::weak_ptr~routing_host~ routing_host_
}
endpoint <|-- endpoint_impl : Inheritance
endpoint_impl --> endpoint_host : Association
endpoint_impl --> routing_host : Association
vsomeip对于各个模块定义了xxx_host类,xxx_host类并不是该模块的基类,xxx_host类是其他模块的基类。该模块可通过指向xxx_host的指针,访问其他模块。例如:sd模块中有service_discovery_host类,而service_discovery_host是routing_manager_impl的基类。service_discovery_impl类中有以下成员变量
1
service_discovery_host *host_
然后service_discovery_impl可以通过此指针访问routing_manager_impl类。
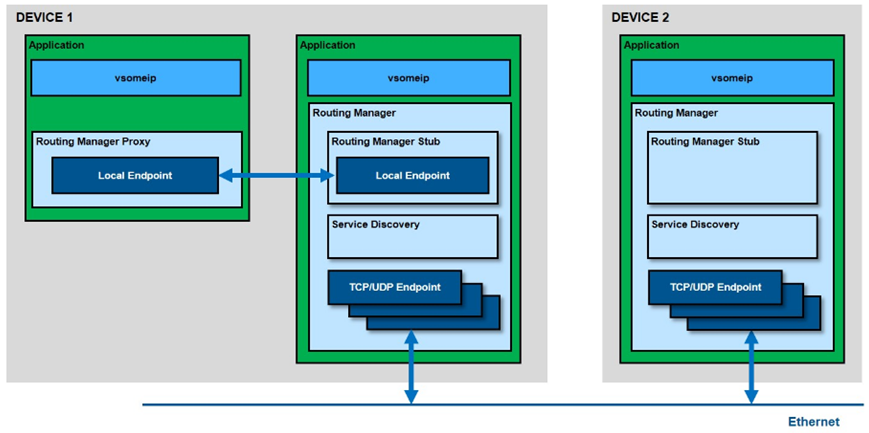
Host和Proxy模式
在用户调用了application::init()函数后,vsomeip会执行一下部分代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
std::string its_routing_host = its_configuration->get_routing_host_name();
if (its_routing_host != "") {
is_routing_manager_host_ = (its_routing_host == name_);
if (is_routing_manager_host_ &&
!utility::is_routing_manager(configuration_->get_network())) {
#ifndef VSOMEIP_ENABLE_MULTIPLE_ROUTING_MANAGERS
VSOMEIP_ERROR << "application: " << name_ << " configured as "
"routing but other routing manager present. Won't "
"instantiate routing";
is_routing_manager_host_ = false;
return false;
#else
is_routing_manager_host_ = true;
#endif // VSOMEIP_ENABLE_MULTIPLE_ROUTING_MANAGERS
}
} else {
auto its_routing_address = its_configuration->get_routing_host_address();
auto its_routing_port = its_configuration->get_routing_host_port();
if (its_routing_address.is_unspecified()
|| is_local_endpoint(its_routing_address, its_routing_port))
is_routing_manager_host_ = utility::is_routing_manager(configuration_->get_network());
}
vsomeip会根据配置文件中routing字段是否是本次运行的app name(app name可以通过环境变量VSOMEIP_APPLICATION_NAME设置),选择启用Host模式还是Proxy模式。而Host和Proxy实际上只是创建的routing_manger类不同。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
if (is_routing_manager_host_) {
VSOMEIP_INFO << "Instantiating routing manager [Host].";
if (client_ == VSOMEIP_CLIENT_UNSET) {
client_ = static_cast<client_t>(
(configuration_->get_diagnosis_address() << 8)
& configuration_->get_diagnosis_mask());
utility::request_client_id(configuration_, name_, client_);
}
routing_ = std::make_shared<routing_manager_impl>(this);
} else {
VSOMEIP_INFO << "Instantiating routing manager [Proxy].";
routing_ = std::make_shared<routing_manager_client>(this, client_side_logging_, client_side_logging_filter_);
}
对于Host模式,创建routing_manager_impl类,对于Proxy模式,创建routing_manager_client类。在routing_manager_client类中并没有创建sd模块,也没有endpoint manager模块。那么Proxy模式下,如何实现someip的各个功能呢?
在routing_manager_client创建两个本地UDS通信的endpoint,一个用于发送,一个用于接受。如下所示:
1
2
std::shared_ptr<endpoint> sender_; // --> stub
std::shared_ptr<endpoint> receiver_; // --> from everybody
1
2
3
sender_ = ep_mgr_->create_local(VSOMEIP_ROUTING_CLIENT);
...
receiver_ = ep_mgr_->create_local_server(shared_from_this());
这两个对象会与routing_manager_stub类进行通信。而routing_manager_stub类的对象会在routing_manager_impl类中创建。如下:
1
2
std::shared_ptr<routing_manager_stub> stub_;
stub_ = std::make_shared<routing_manager_stub>(this, configuration_);
Proxy模式下Event分析
event订阅
注册订阅
在routing_manager_client类,无论是请求订阅,还是提供订阅,都是调用routing_manager_client::register_event来实现的。routing_manager_client::register_event的函数声明如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
virtual void register_event(client_t _client,
service_t _service, instance_t _instance,
event_t _notifier,
const std::set<eventgroup_t> &_eventgroups,
const event_type_e _type, reliability_type_e _reliability,
std::chrono::milliseconds _cycle, bool _change_resets_cycle,
bool _update_on_change, epsilon_change_func_t _epsilon_change_func,
bool _is_provided, bool _is_shadow = false,
bool _is_cache_placeholder = false)
可通过_is_provided来区分是请求订阅还是提供订阅。
register_event函数最后会调用routing_manager_client::send_register_event发送订阅。
send_register_event的函数声明如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
void send_register_event(client_t _client,
service_t _service, instance_t _instance,
event_t _notifier,
const std::set<eventgroup_t> &_eventgroups,
const event_type_e _type, reliability_type_e _reliability,
bool _is_provided, bool _is_cyclic)
send_register_event最终会调用sender_->send(&its_buffer[0], uint32_t(its_buffer.size()))将event的订阅消息发送给本机上在Host模式下运行的vsomeip应用。
Host模式下运行的vsomeip应用会在routing_manager_stub类的on_message函数中收到此event的订阅消息,并进行相应的处理,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
case protocol::id_e::REGISTER_EVENT_ID:
{
protocol::register_events_command its_command;
its_command.deserialize(its_buffer, its_error);
if (its_error == protocol::error_e::ERROR_OK) {
its_client = its_command.get_client();
for(std::size_t i = 0; i < its_command.get_num_registrations(); i++) {
protocol::register_event register_event;
if (!its_command.get_registration_at(i, register_event)) {
continue;
}
its_service = register_event.get_service();
its_instance = register_event.get_instance();
if (register_event.is_provided()
&& !configuration_->is_offered_remote(its_service, its_instance)) {
continue;
}
host_->register_shadow_event(its_client,
its_service, its_instance,
register_event.get_event(), register_event.get_eventgroups(),
register_event.get_event_type(), register_event.get_reliability(),
register_event.is_provided(), register_event.is_cyclic());
...
}
} else
VSOMEIP_ERROR << __func__ << ": register event deserialization failed ("
<< std::dec << static_cast<int>(its_error) << ")";
break;
}
可以看到最终调用了host_->register_shadow_event函数,host_是指向routing_manager_impl的指针,实际上就是调用的routing_manager_impl::register_shadow_event函数。而routing_manager_impl::register_shadow_event最终会调用routing_manager_base::register_event函数。
客户端请求订阅
如果是请求订阅,则还需要调用routing_manager_client::subscribe函数,声明如下:
1
2
3
4
void subscribe(client_t _client, const vsomeip_sec_client_t *_sec_client,
service_t _service, instance_t _instance,
eventgroup_t _eventgroup, major_version_t _major,
event_t _event, const std::shared_ptr<debounce_filter_impl_t> &_filter)
routing_manager_client::subscribe会调用routing_manager_client::send_subscribe将消息发送出去。routing_manager_client::send_subscribe声明如下:
1
2
3
4
void send_subscribe(client_t _client,
service_t _service, instance_t _instance,
eventgroup_t _eventgroup, major_version_t _major,
event_t _event, const std::shared_ptr<debounce_filter_impl_t> &_filter)
同样的,Host模式下运行的vsomeip应用会在routing_manager_stub类的on_message函数中收到此event的subscribe消息,并进行相应的处理,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
case protocol::id_e::SUBSCRIBE_ID:
{
protocol::subscribe_command its_command;
its_command.deserialize(its_buffer, its_error);
if (its_error == protocol::error_e::ERROR_OK) {
its_client = its_command.get_client();
its_service = its_command.get_service();
its_instance = its_command.get_instance();
its_eventgroup = its_command.get_eventgroup();
its_major = its_command.get_major();
its_notifier = its_command.get_event();
auto its_filter = its_command.get_filter();
if (its_notifier == ANY_EVENT) {
if (host_->is_subscribe_to_any_event_allowed(_sec_client, its_client, its_service,
its_instance, its_eventgroup)) {
host_->subscribe(its_client, _sec_client, its_service, its_instance,
its_eventgroup, its_major, its_notifier, its_filter);
} else {
VSOMEIP_WARNING << "vSomeIP Security: Client 0x" << std::hex << its_client
<< " : routing_manager_stub::on_message: "
<< " subscribes to service/instance/event "
<< its_service << "/" << its_instance << "/ANY_EVENT"
<< " which violates the security policy ~> Skip subscribe!";
}
} else {
if (VSOMEIP_SEC_OK == security::is_client_allowed_to_access_member(
_sec_client, its_service, its_instance, its_notifier)) {
host_->subscribe(its_client, _sec_client, its_service, its_instance,
its_eventgroup, its_major, its_notifier, its_filter);
} else {
VSOMEIP_WARNING << "vSomeIP Security: Client 0x" << std::hex << its_client
<< " : routing_manager_stub::on_message: "
<< " subscribes to service/instance/event "
<< its_service << "/" << its_instance << "/" << its_notifier
<< " which violates the security policy ~> Skip subscribe!";
}
}
} else
VSOMEIP_ERROR << __func__
<< ": deserializing subscribe failed ("
<< std::dec << static_cast<int>(its_error) << ")";
break;
}
最终调用了host_->subscribe函数。而host_->subscribe实际上就是routing_manager_impl::subscribe,这样就和Host模式xAI的subscribe的处理流程一样了。
客户端处理subscribeack
Host模式下运行的vsomeip应用收到了subscribeack消息后,会进行判断:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
void routing_manager_impl::on_subscribe_ack(client_t _client,
service_t _service, instance_t _instance, eventgroup_t _eventgroup,
event_t _event, remote_subscription_id_t _id) {
...
for (const auto &its_subscriber : subscribed_clients) {
if (its_subscriber == get_client()) {
if (_event == ANY_EVENT) {
for (const auto &its_event : its_eventgroup->get_events()) {
host_->on_subscription_status(_service, _instance,
_eventgroup, its_event->get_event(),
0x0 /*OK*/);
}
} else {
host_->on_subscription_status(_service, _instance,
_eventgroup, _event, 0x0 /*OK*/);
}
} else if (stub_) {
stub_->send_subscribe_ack(its_subscriber, _service,
_instance, _eventgroup, _event);
}
}
}
}
当client id不是本app的client id的时候,会通过routing_manager_stub::send_subscribe_ack将ack消息发送出去。
routing_manager_stub::send_subscribe_ack的声明如下:
1
2
void send_subscribe_ack(client_t _client, service_t _service,
instance_t _instance, eventgroup_t _eventgroup, event_t _event)
在send_subscribe_ack的函数,会将subscribe_ack消息返回。
Proxy模式下,routing_manager_client首先会在routing_manager_client::on_message函数对收到的subscribe_ack进行处理。routing_manager_client::on_message的声明如下:
1
2
3
4
5
void on_message(const byte_t *_data, length_t _size, endpoint *_receiver,
bool _is_multicast,
client_t _bound_client, const vsomeip_sec_client_t *_sec_client,
const boost::asio::ip::address &_remote_address,
std::uint16_t _remote_port)
处理的代码片段如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
case protocol::id_e::SUBSCRIBE_ACK_ID:
{
protocol::subscribe_ack_command its_subscribe_ack;
its_subscribe_ack.deserialize(its_buffer, its_error);
if (its_error == protocol::error_e::ERROR_OK) {
its_service = its_subscribe_ack.get_service();
its_instance = its_subscribe_ack.get_instance();
its_eventgroup = its_subscribe_ack.get_eventgroup();
its_subscriber = its_subscribe_ack.get_subscriber();
its_event = its_subscribe_ack.get_event();
on_subscribe_ack(its_subscriber, its_service, its_instance, its_eventgroup, its_event);
VSOMEIP_INFO << "SUBSCRIBE ACK("
<< std::hex << std::setfill('0')
<< std::setw(4) << its_client << "): ["
<< std::setw(4) << its_service << "."
<< std::setw(4) << its_instance << "."
<< std::setw(4) << its_eventgroup << "."
<< std::setw(4) << its_event << "]";
} else
VSOMEIP_ERROR << __func__
<< ": subscribe ack command deserialization failed ("
<< std::dec << static_cast<int>(its_error) << ")";
break;
}
可以看到最后又routing_manager_client::on_subscribe_ack进行了处理。
Host模式下Event分析
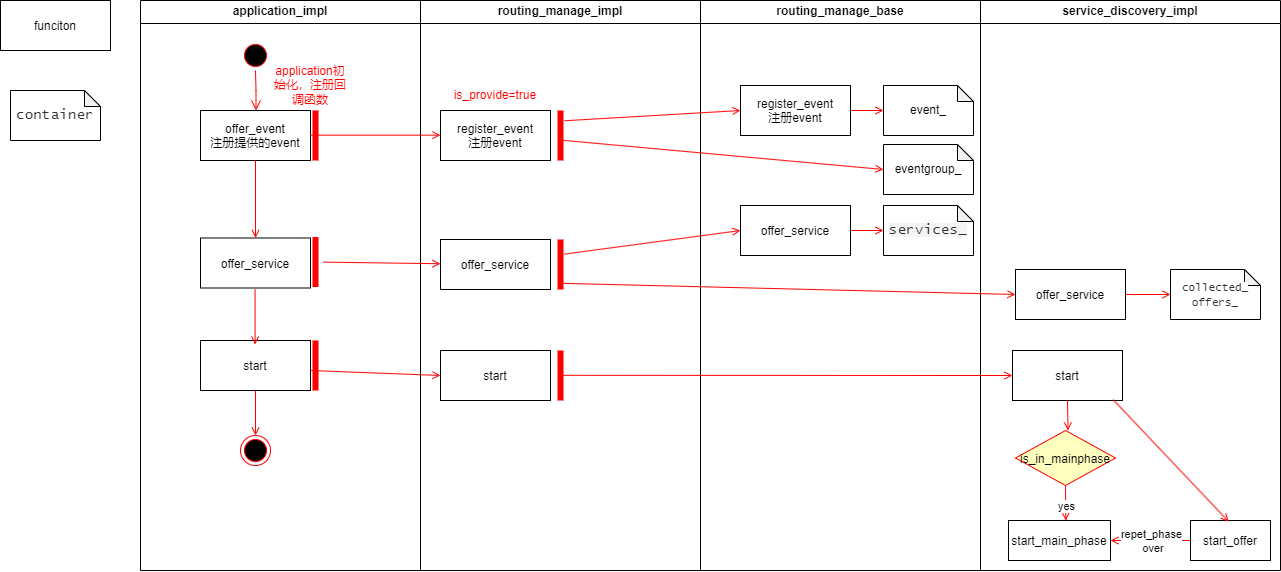
服务端提供订阅
Application层
- 首先创建并初始化application,然后调用
application_impl->register_message_handler注册事件field相关的set和get方法。 - 调用
application_impl->offer_event向外提供对应的event或field。 - 调用
application_impl->offer_service向外提供对应的服务实例。 - 调用
application_impl->start启动函数。
RoutingManger层
在application_impl->offer_event内,会调用routing_manager_impl->register_event函数注册对应的event(注:在此过程中,register_event(… bool is_provided…)_中is_provided会赋值为true,注意与客户端请求event对比)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
routing_->register_event(client_,_service, _instance,
_notifier, _eventgroups, _type, _reliability,
_cycle, _change_resets_cycle, _update_on_change,
_epsilon_change_func, true);
//该函数原型
void routing_manager_impl::register_event(vsomeip_v3::client_t _client, vsomeip_v3::service_t _service, vsomeip_v3::instance_t _instance, vsomeip_v3::event_t _notifier,
const std::set<...> &_eventgroups, vsomeip_v3::event_type_e _type, vsomeip_v3::reliability_type_e _reliability, std::chrono::milliseconds _cycle, bool _change_resets_cycle, bool _update_on_change, vsomeip_v3::epsilon_change_func_t _epsilon_change_func, bool _is_provided, bool _is_shadow = false, bool _is_cache_placeholder = false)
//相关变量赋为:
_cycle std::chrono::milliseconds::zero()
_change_resets_cycle false
_update_on_change true
_epsilon_change_func nullptr
_is_provided = true
bool _is_shadow = false, bool _is_cache_placeholder = false
具体routing_manager_impl::register_event函数调用运行如下:
首先会调用在
routing_manager_impl::events_容器中查找是否为首次注册,若是,则调用routing_manager_base::register_event进行注册对于event的传输(reliability)是udp还是tcp或其他,优先以配置文件为准;配置文件若为
RT_UNKNOWN类型,则以调用该注册函数传参为准;若传参仍为RT_UNKNOWN,则以服务的reliability为准。再次在
routing_manager_base::events_容器中查找,若event已存在且不是缓存占位符,且类型与注册的相同(或已注册的类型为ET_UNKNOWN),则更新event相关参数,同时将其添加到指定的eventgroups中(调用application_impl->offer_event时传入的eventgroups),transfer_subscriptions_from_any_event变量为true;若已存在且是缓存占位符,则根据传参赋值,若event不是field类型,则不预设payload值。若eventgroup为空,则初始化一个插入:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
if (_type != event_type_e::ET_FIELD) { // don't cache payload for non-fields its_event->unset_payload(true); } if (_eventgroups.size() == 0) { // No eventgroup specified std::set<eventgroup_t> its_eventgroups; its_eventgroups.insert(_notifier); its_event->set_eventgroups(its_eventgroups); }
若不存在,则根据传参创建一个event(这部分中间
if ((_is_shadow || is_routing_manager()) && !_epsilon_change_func)分支作用未懂)若之前设置
transfer_subscriptions_from_any_event=true或_is_provided=true,将从ANY_EVENT转移订阅到创建的event遍历传入的eventgroups容器,在
routing_manager_base::eventgroups_容器中查找eventgroups中每个eventgroup,若不存在,则根据传参创建一个eventgroup存入routing_manager_base::eventgroups_容器中。然后向对应的eventgroup添加event信息(注:之前是向创建的event类中添加对应的eventgroup,现在是向routing_manager_base::eventgroups_容器中添加对应的event)最后向
routing_manager_base::events_容器中添加对应的event
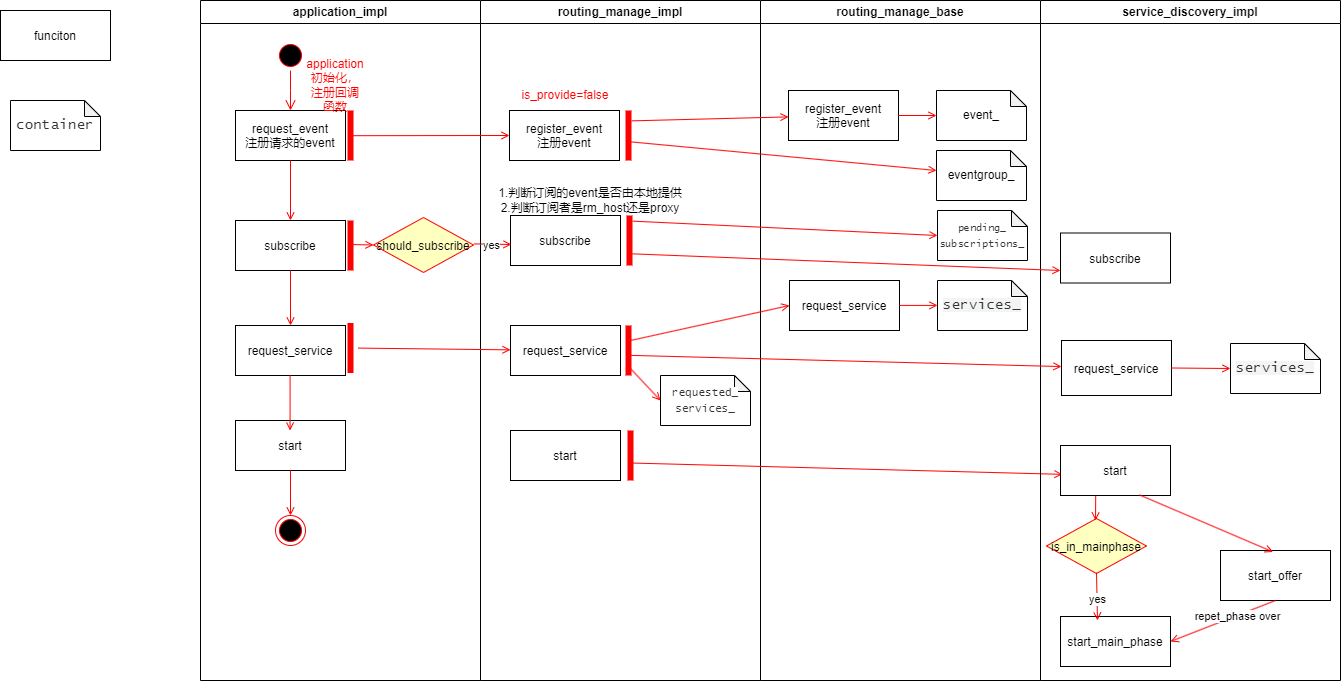
客户端请求订阅
Application层
首先创建并初始化application,然后调用
application_impl->register_message_handler注册相关method。调用
application_impl->request_event向外请求对应的event或field调用
application_impl->subscribe向外订阅event获field调用
application_impl->request_service请求服务调用
application_impl->start启动函数
RoutingManger层
在application_impl->request_event中
直接调用routing_manager_impl->register_event函数注册event(注意与服务端对比,区别在于_is_provided变量为false):
1
2
3
4
5
routing_->register_event(client_,_service, _instance,
_event, _eventgroups, _type, _reliability,
std::chrono::milliseconds::zero(), false, true,
nullptr,
false);
针对请求的event注册,此处不在赘述。
在application_impl->subscribe中,该函数声明为:
1
2
3
void vsomeip_v3::application::subscribe(vsomeip_v3::service_t _service,
vsomeip_v3::instance_t _instance, vsomeip_v3::eventgroup_t _eventgroup, vsomeip_v3::major_version_t _major = (vsomeip_v3::major_version_t)0U,
vsomeip_v3::event_t _event = (vsomeip_v3::event_t)65535U)
注:_event传参默认值为(vsomeip_v3::event_t)65535U,代表为ANY_EVENT
使能了
routing_则会调用application_impl::check_send_back_cached_event该函数内,会在
application_impl::subscriptions_map容器中查找对应的[_service][_instance][_event][_eventgroup]键值对是否存在:若不存在subscriptions_[_service][_instance][_event][_eventgroup]=false;若存在且对应的值为true,则进一步判断,更改传入的bool指针值:1 2 3 4 5
if(_event == ANY_EVENT) { *_send_back_cached_eventgroup = true; } else { *_send_back_cached_event = true; }
后续会依据这些判断调用对应的函数:
1 2 3 4 5
if (send_back_cached) { send_back_cached_event(_service, _instance, _event); } else if(send_back_cached_group) { send_back_cached_eventgroup(_service, _instance, _eventgroup); }
这种实际上并不会向外发布subscribe消息。
之后调用
application_impl::check_subscription_state函数: 该函数内,首先在application_impl::subscription_state_容器内查找对应的[_service][_instance][_eventgroup][_event]键值对是否存在:若存在,则进一步根据订阅状态做判断:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
if (its_event->second != subscription_state_e::SUBSCRIPTION_NOT_ACKNOWLEDGED) { has_found = true; should_subscribe = false; if (its_event->second == subscription_state_e::SUBSCRIPTION_ACKNOWLEDGED) { is_acknowledged = true; } }
若不存在,就改变对应的订阅状态为
IS_SUBSCRIBING:1 2 3 4
if (!has_found) { subscription_state_[_service][_instance][_eventgroup][_event] = subscription_state_e::IS_SUBSCRIBING; }
同时传递订阅状态
[!CAUTION]
(该函数代码过长,未搞清楚)
1 2 3
if (!should_subscribe && is_acknowledged) { deliver_subscription_state(_service, _instance, _eventgroup, _event, 0 /* OK */); }
最后返回
should_subscribe是否需要订阅。若上一步的返回值为true,则调用
routing_manager_impl::subscribe进行订阅。
至此,application_impl->subscribe函数结束。
在routing_manager_impl::subscribe函数中:
1 2 3
--->rm_impl::find_local_client(_service, _instance); --->...... --->rm_base::find_local_client_unlocked(_service, _instance);
最后会在
routing_manager_impl::local_services_中查找对应的服务、实例的client若查找返回的client与
routing_manager_base::client_相同[!CAUTION]
应该是判断为本地routing manager自身提供的服务,具体的流程暂未深究
若不相同,则准备调用sd模块发送
1
insert_subscription(_service, _instance, _eventgroup,_event, _filter, _client, &its_already_subscribed_events);
若传参
_event != ANY_EVENT,则调用routing_manager_base::find_event(_service, _instance, _event)查找对应的event,然后添加订阅者:1 2
is_inserted = its_event->add_subscriber(_eventgroup, _filter, _client, host_->is_routing());
并返回结果
is_inserted。[!CAUTION]
若没有查找到对应的event,则:
1 2
is_inserted = create_placeholder_event_and_subscribe(_service, _instance, _eventgroup, _event, _filter, _client);
然后返回结果
is_inserted。该函数暂未搞清楚,应该是创建占位符若传参
_event == ANY_EVENT,则调用routing_manager_base::find_eventgroup(_service, _instance, _eventgroup)在对应的routing_manager_base::eventgroups_查找对应的eventgroup,然后从对应的eventgroup中读取events,遍历每个event,添加订阅者:1 2
is_inserted = e->add_subscriber(_eventgroup, _filter, _client, host_->is_routing()) || is_inserted;
同时,若event已被_client订阅(通过其他事件组订阅),则将对应event插入
_already_subscribed_events容器中。[!CAUTION]
若没有找到对应的eventgroup或者eventgroup中没有event,则:
1 2
is_inserted = create_placeholder_event_and_subscribe(_service, _instance, _eventgroup, _event, _filter, _client);
然后返回结果
is_inserted。
若之前在
routing_manager_impl::local_services_中查找对应的服务、实例的client=0,则1 2 3 4
handle_subscription_state(_client, _service, _instance, _eventgroup, _event); static const ttl_t configured_ttl(configuration_->get_sd_ttl()); notify_one_current_value(_client, _service, _instance, _eventgroup, _event, its_already_subscribed_events);
若在
routing_manager_base::eventgroups_容器中查找到对应eventgroup信息,且(订阅者不是host或者在routing_manager_base::services_容器中查找到对应服务,则通过service_discovery_impl::subscribe发送订阅 若在routing_manager_impl::local_services_中查找对应的服务、实例的client不为0,则通过stub_->send_subscribe发送订阅信息- 订阅者若是host,则将订阅信息插入
routing_manager_base::pending_subscriptions_容器
至此,routing_manager_impl::subscribe函数结束。
event的发送
首先在app层面调用notify后,如下:
1
2
app_ = vsomeip::runtime::get()->create_application()
app_->notify(SAMPLE_SERVICE_ID, SAMPLE_INSTANCE_ID,SAMPLE_EVENT_ID, payload_);
notify函数原型为:
1
2
3
4
//源码的interface目录内的application.hpp文件内声明
virtual void notify(service_t _service, instance_t _instance,
event_t _event, std::shared_ptr<payload> _payload,
bool _force = false) const = 0;
application_impl->notify最终会调用routing_manager_base->notify函数,在routing_manager_base::events_容器中查找对应的event,然后调用对应event的event->set_payload函数发送
1
2
3
4
5
event->set_payload{
-->notify
-->if (change_resets_cycle_)
start_cycle();
}
在void event::notify(bool _force)函数中,会调用routing_->send(VSOMEIP_ROUTING_CLIENT, update_, _force)函数发送notify报文,同时start_cycle函数开启循环发送的定时器。
下面针对send具体讲解,最终会调用routing_manager_impl::send函数:
1
2
3
4
bool routing_manager_impl::send(client_t _client, const byte_t *_data,
length_t _size, instance_t _instance, bool _reliable,
client_t _bound_client, const vsomeip_sec_client_t *_sec_client,
uint8_t _status_check, bool _sent_from_remote, bool _force)
函数内会进行一系列检查,针对notification报文,会依据传入的服务、实例、method找到对应的event,然后依据event找到对应的所有eventgroups,然后依据eventgroup中的subscriptions_容器内的订阅信息获取每个订阅者信息,然后发送。
服务端event的处理
启动后,服务端会一直通过多播向外发送offerservice。客户端也会发送find多播报文或者subscribe报文。收到的消息经由以下函数处理:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
--->routing_manager_impl::on_message(const byte_t *_data, length_t _size,......)
/...code.../
--->service_discoery_impl::on_message(const byte_t *_data, length_t _length,......)
/...code.../
--->service_discoery_impl::process_eventgroupentry(its_eventgroup_entry,...,its_acknowledgement,...)
/...code.../ //解析报文处理结果并进一步处理,应答或忽略
/...code.../
--->routing_manager_impl::on_message(service_t _service, instance_t _instance,......)//非sd报文由该函数处理
//end
在service_discoery_impl::process_eventgroupentry函数解析,函数原型如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
void service_discovery_impl::process_eventgroupentry(
std::shared_ptr<eventgroupentry_impl> &_entry,
const std::vector<std::shared_ptr<option_impl> > &_options,
std::shared_ptr<remote_subscription_ack> &_acknowledgement,
const boost::asio::ip::address &_sender,
bool _is_multicast,
bool _is_stop_subscribe_subscribe, bool _force_initial_events,
const sd_acceptance_state_t& _sd_ac_state)
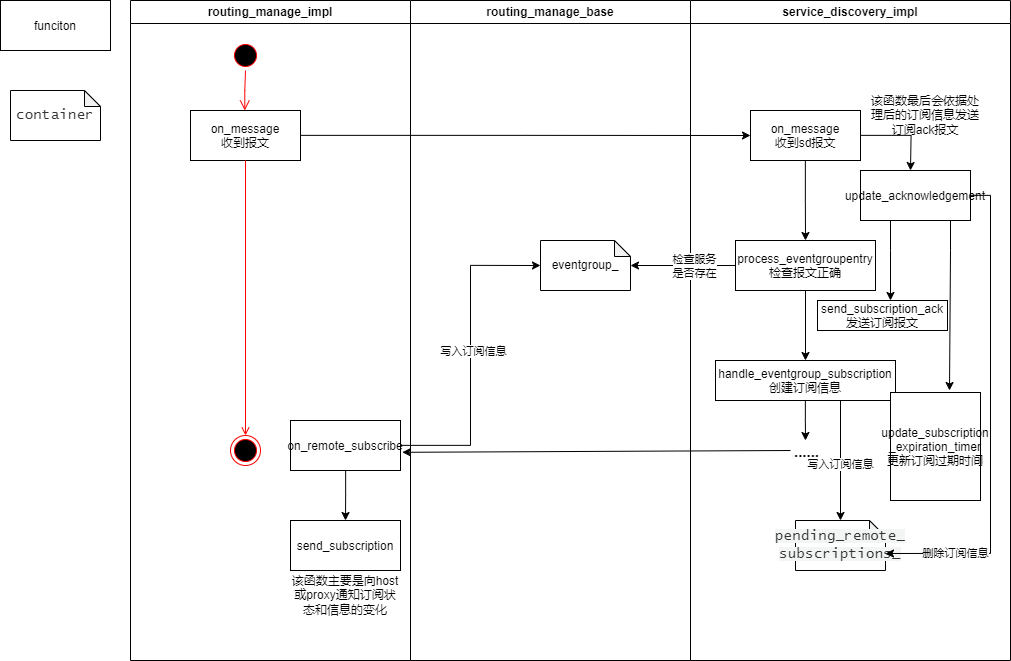
在service_discoery_impl::handle_eventgroup_subscription函数中:
解析entry信息,通过层层调用
routing_manager_base::find_eventgroup函数查找eventgroups_容器内是否有相关信息,若没有记录:- 且entry类型为
SUBSCRIBE_EVENTGROUP以及该entry的ttl大于0,那么就设置ttl为0,向_acknowledgement插入订阅nack报文 - 若不是
SUBSCRIBE_EVENTGROUP,就调用service_discovery_impl::unsubscribe函数在subscribed_容器中查找,然后解除订阅并发送message消息
做完以上,直接return返回
- 且entry类型为
检查entry对应的报文的
return_code对于entry类型为
SUBSCRIBE_EVENTGROUP报文,会对其地址、entry字段的option数量、等等字段长度做检查,如有问题会报错直接返回或回复一个nack。对entry内提及的option数量是否与options数量对应,若options数量少于entry内说的,会报错并回复nack,然后直接返回
之后会检查每个options的类型,调用sd_impl模块的
check_layer_four_protocol函数检查ip是否正确,并随之根据options内提及的端口信息配置its_first_address、its_second_address等局部变量(注:针对option类型为:CONFIGURATION,会不做任何处理)最后会依据具体的类型,转交给sd_impl模块的
handle_eventgroup_subscription函数处理,SUBSCRIBE_EVENTGROUP_ACK转交给sd_impl模块的handle_eventgroup_subscription_ack函数或handle_eventgroup_subscription_nack函数。
针对SUBSCRIBE_EVENTGROUP调用handle_eventgroup_subscription函数处理,该函数原型为:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
void service_discovery_impl::handle_eventgroup_subscription(
service_t _service, instance_t _instance,
eventgroup_t _eventgroup, major_version_t _major,
ttl_t _ttl, uint8_t _counter, uint16_t _reserved,
const boost::asio::ip::address &_first_address, uint16_t _first_port,
bool _is_first_reliable,
const boost::asio::ip::address &_second_address, uint16_t _second_port,
bool _is_second_reliable,
std::shared_ptr<remote_subscription_ack> &_acknowledgement,
bool _is_stop_subscribe_subscribe, bool _force_initial_events,
const std::set<client_t> &_clients,
const sd_acceptance_state_t& _sd_ac_state,
const std::shared_ptr<eventgroupinfo>& _info)
在service_discovery_impl::handle_eventgroup_subscription函数中:
判断
_entry字段的版本信息与自己提供的是否一致创建订阅者的端口,判断端口是
udp multicast、tcp unicast还是udp unicast依据订阅者的端口信息,创建
remote_subscription类型指针并赋值,若
_ttl=0,且_is_stop_subscribe_subscribe=false(_is_stop_subscribe_subscribe变量在sd_impl->on_message函数中通过check_stop_subscribe_subscribe函数赋值,若ttl=0、且entry为停止订阅类型、且message中后续的entries又有请求订阅的entry,则该变量为true),会向容器pending_remote_subscriptions_中添加ack:1 2
pending_remote_subscriptions_[its_subscription] = _acknowledgement; host_->on_remote_unsubscribe(its_subscription);
然后返回。
后续会进行
_force_initial_events判断最后会如同ttl=0操作一样插入
_acknowledgement变量,然后调用rm_impl->on_remote_subscribe函数:1 2 3
host_->on_remote_subscribe(its_subscription, std::bind(&service_discovery_impl::update_remote_subscription, shared_from_this(), std::placeholders::_1));
在
on_remote_subscribe函数中,依据ttl和现在时间计算失效时间,更新订阅信息,刷新订阅时间。调用
eventgroupinfo::update_remote_subscription函数更新订阅信息,若不是一个新订阅,且是个重复订阅,没有改变,则直接调用回调函数sd_impl->update_remote_subscription,然后函数运行结束,该分支过多,暂未弄清。至此,
rm_impl::on_remote_subscribe结束
至此,process_eventgroupentry函数处理完毕
处理完报文中每个entry后,针对eventgroupentry处理的结果its_acknowledgement,会调用update_acknowledgement与send_subscription_ack函数处理和发送。其中,在update_acknowledgement函数内,也是会调用send_subscription_ack函数发送结果,而在send_subscription_ack函数内,调用update_subscription_expiration_timer函数更新定时器,具体为:
- 首先更新订阅过期时间
- 调用
start_subscription_expiration_timer_unlocked函数:- 该函数会延时
next_subscription_expiration_异步调用sd_impl::expire_subscriptions函数,后续调来调去,最后会调用rm_impl::expire_subscriptions(bool force)函数,若订阅期满,会获取之前在rm_impl->on_remote_subscribe函数内赋值的过期时间点,然后与现在时刻对比,进一步判断是否过期,后续一大段都是对过期订阅的处理
- 该函数会延时
客户端event的处理
客户端重复发送event订阅报文的逻辑和收到offer service报文相关。
在sd模块的on_message函数中,声明如下:
1
2
3
4
5
void
service_discovery_impl::on_message(
const byte_t *_data, length_t _length,
const boost::asio::ip::address &_sender,
const boost::asio::ip::address &_destination)
在on_message的处理中,会创建以下变量:
1
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<message_impl> > its_resubscribes;
如果收到的报文为service报文,则会将此变量传递至service_discovery_impl::process_serviceentry函数处理,如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
...
if ((*iter)->is_service_entry()) {
std::shared_ptr<serviceentry_impl> its_service_entry
= std::dynamic_pointer_cast<serviceentry_impl>(*iter);
bool its_unicast_flag = its_message->get_unicast_flag();
process_serviceentry(its_service_entry, its_options,
its_unicast_flag, its_resubscribes,
_is_multicast, accept_state);
} else {
...
}
process_serviceentry的声明如下:
1
2
3
4
void process_serviceentry(std::shared_ptr<serviceentry_impl> &_entry,
const std::vector<std::shared_ptr<option_impl> > &_options,
bool _unicast_flag, std::vector<std::shared_ptr<message_impl> > &_resubscribes,
bool _received_via_mcast, const sd_acceptance_state_t& _sd_ac_state);
process_serviceentry函数中,会对entry类型进一步判断。当ttl > 0,且entry的类型为offer service的时候,会将_resubscribes传递至service_discovery_impl::process_offerservice_serviceentry函数。service_discovery_impl::process_offerservice_serviceentry的声明如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
void process_offerservice_serviceentry(
service_t _service, instance_t _instance, major_version_t _major,
minor_version_t _minor, ttl_t _ttl,
const boost::asio::ip::address &_reliable_address,
uint16_t _reliable_port,
const boost::asio::ip::address &_unreliable_address,
uint16_t _unreliable_port,
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<message_impl> > &_resubscribes,
bool _received_via_mcast, const sd_acceptance_state_t& _sd_ac_state);
在process_offerservice_serviceentry函数最后,会判断本次offer service报文是否是有多播发送。如果判断为多播方式的发送,则从service_discovery_impl::subscribed_变量中查找本服务相关的event订阅信息,然后将相关的event订阅信息放入_resubscribes变量。而_resubscribes定义是在service_discovery_impl::on_message中。
在service_discovery_impl::on_message的最后,会对its_resubscribes进行判断:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
for (auto iter = its_resubscribes.begin(); iter != its_resubscribes.end();) {
if ((*iter)->get_entries().empty() || (*iter)->get_options().empty()) {
iter = its_resubscribes.erase(iter);
} else {
iter++;
}
}
if (!its_resubscribes.empty()) {
serialize_and_send(its_resubscribes, _sender);
}
当its_resubscribes不为空的时候,会调用serialize_and_send进行发送。